
Other Causes of Chest Pain After Eating Esophageal UlcersĮsophageal ulcers can form as a result of GERD or certain kinds of infections. This can result in pain in the chest cavity, which often increases after eating.

A hiatal hernia occurs when the upper part of the stomach protrudes through the hole in the diaphragm and into the chest cavity. The esophagus passes through a hole in the diaphragm to reach the stomach through the chest cavity. The diaphragm muscle is what separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity. There is currently no cure for this disorder, but it can be managed with proper treatment. This causes difficulty in swallowing and passing food to the stomach and can result in pain in the chest where the food is attempting to pass. The condition is a result of damage to the nerves in the esophagus, making the muscles in the tube looser. AchalasiaĪchalasia is a rare medical condition that occurs when the stomach has difficulty passing liquid or food. This can also occur if a patient is suffering from food poisoning. Be aware of your food sensitivities and if these are related to experiencing gas pain in the chest. The most common cause of this is food sensitivities or intolerances. Gas pain in the chest occurs when there is a buildup of gas in the digestive tract, resulting in pain in the chest. GERD can cause severe complications if left untreated, and medical advice should be sought. If you suffer from heartburn after eating, at least twice a week for several weeks, you may have GERD. This is colloquially referred to as heartburn. Acid reflux from the stomach into the throat is one of the most common causes of chest pain that occurs after eating. GERD is the medical term for chronic acid reflux. This can occur due to the consumption of fatty foods and can result in tightness and pain in the chest, especially after eating. Gallbladder AttackĪ gallbladder attack occurs when a gallstone, created in the gallbladder, gets lodged in one of the bile ducts in the intestines, causing a decrease in the flow of bile. When a person overeats, there is increased pressure in the stomach and digestive tract, which can result in chest pain. It is possible to lose track of how much we have eaten or to simply eat too quickly to give our digestive tract the necessary time to indicate fullness. Chest pain is the result of the increased pressure in the lungs and throat from the swelling. The immune response to an allergic reaction is for cells to produce histamines, which cause inflammation. The cause of the pain is generally due to the tightening of the throat and the lungs caused by the allergic reaction. Food AllergiesĪ food allergy may result in chest pain after consumption of the allergen. More serious common causes are mentioned below. The most common and benign causes of chest pain after eating include swallowing too large a bite of food or consuming something too hot or cold. If any of the following symptoms are experienced, contact emergency services: shortness of breath, pain that intensifies and does not respond to antacids, dizziness or fainting, severe nausea, vomiting (especially projectile vomiting or bloody vomiting), or intense abdominal pain. If the pain persists, however, it may be indicative of an underlying cause and medical attention should be sought. For most, the sensation of chest pain is short-term and will resolve itself without the need for medical intervention.
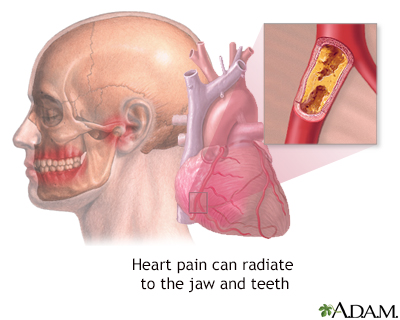

There are many potential causes of chest pain in association with eating and these will be discussed later in this article. Suffering from chest pain during or after eating is not uncommon, unfortunately.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
